
ASST.PROF. PHORRAMATPANYAPRAT TONGPRASONG, Ph.D., FHEA UKPSF
》》》》》》》》》》
August, 2025 [PDF]
วงจรการคิด
(Thinking
Circuit)
ประธานการพัฒนาและปรับปรุงหลักสูตรบริหารธุรกิจบัณฑิต
สาขาวิชาธุรกิจสร้างสรรค์และเทคโนโลยีดิจิทัล
คณะวิทยาการจัดการ
มหาวิทยาลัยสวนดุสิต
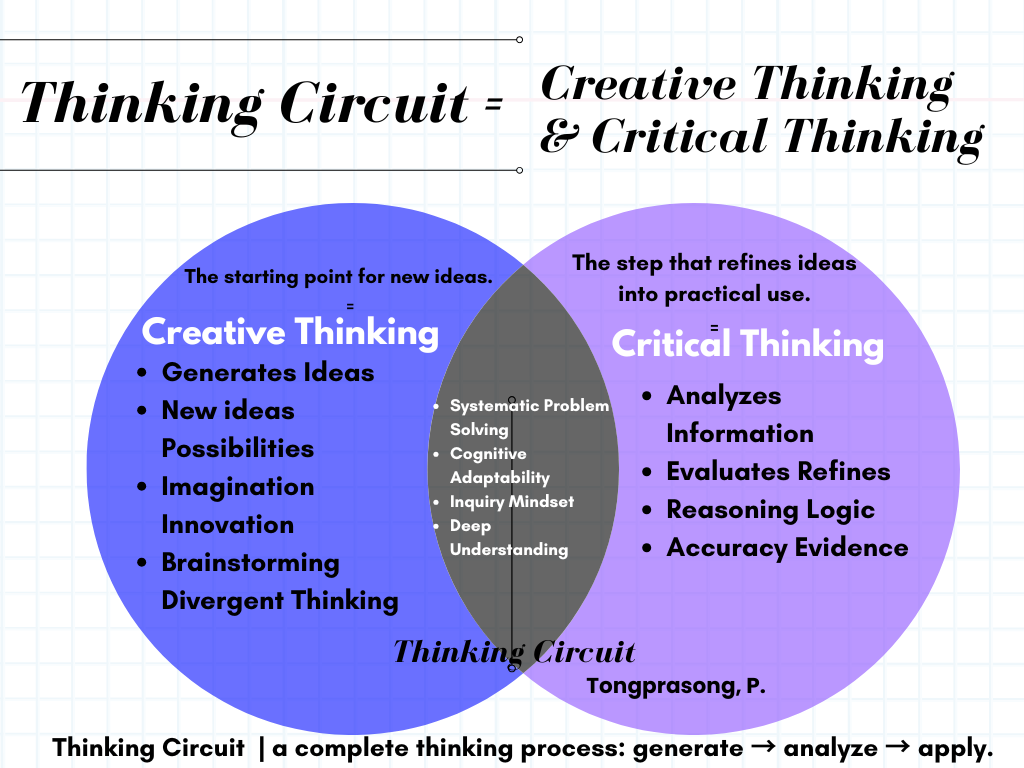
ภาพ
1 Thinking
Circuit: Combination of Creative & Critical Thinking
Thinking Circuit หมายถึง กระบวนการคิดที่เป็นระบบและต่อเนื่องในลักษณะวงจรซึ่งประกอบด้วยขั้นตอนการรับข้อมูล การประมวลผล การวิเคราะห์ และการตัดสินใจ โดยกระบวนการเชื่อมโยงกับการให้ข้อมูลป้อนกลับ (feedback) เพื่อปรับปรุงและพัฒนาคุณภาพของความคิดอย่างต่อเนื่อง ซึ่งทำให้ผู้คิดสามารถเชื่อมโยงองค์ความรู้ใหม่กับประสบการณ์เดิมอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ส่งผลให้เกิดการแก้ปัญหาอย่างสร้างสรรค์และยั่งยืนในบริบทต่าง ๆ
ลักษณะสำคัญของ Thinking Circuit
- เป็นกระบวนการคิดแบบวนซ้ำ (iterative
process) ที่มีการปรับปรุงตนเอง (self-regulation)
- องค์ประกอบหลัก ได้แก่ การรับรู้ข้อมูล (input)
การประมวลผลข้อมูล (processing) การวิเคราะห์และสังเคราะห์ (analysis and synthesis) การตัดสินใจ (decision-making) และการสะท้อนผลลัพธ์
(feedback)
- สนับสนุนการคิดเชิงสร้างสรรค์และเชิงวิพากษ์
โดยการรวมข้อมูลเชิงลึกและมุมมองหลากหลายอย่างสมดุล
- ส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้และการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่อง (continuous learning and improvement)
เมื่อพิจารณา แผนภาพเวนน์ (Venn Diagram) ที่ใช้เปรียบเทียบและแสดงความสัมพันธ์ระหว่าง Creative Thinking (การคิดเชิงสร้างสรรค์) และ Critical Thinking (การคิดเชิงวิพากษ์) โดยมีการแบ่งข้อมูลออกเป็น 3 ส่วนสำคัญจากภาพ 1 ได้ดังนี้
1.
ส่วนเฉพาะของ Creative Thinking (วงกลมสีฟ้าซ้าย)
- Generates
Ideas
- New
Ideas Possibilities
- Imagination
Innovation
- Brainstorming Divergent Thinking
- มุ่งเน้น การสร้างไอเดียและความเป็นไปได้ใหม่ ๆ
- สนับสนุน จินตนาการและนวัตกรรม
- ใช้วิธีการ ระดมสมอง และ คิดแบบแตกแขนง (divergent
thinking)
- ให้ความสำคัญกับ ความแปลกใหม่ ความเสี่ยง และความกล้า
- มองจากหลายมุมมอง และหาทางออกที่ไม่ปกติทั่วไป
- เกิดขึ้นแบบ ทันทีและยืดหยุ่น
- ใช้ในงานศิลปะ การแก้ปัญหา และการสร้างแนวคิด (ideation)
📌
สรุป
เน้น การผลิตไอเดีย แบบไม่จำกัดกรอบ
2.
ส่วนเฉพาะของ
Critical Thinking (วงกลมสีม่วงขวา)
- Analyzes
Information
- Evaluates
Refines
- Reasoning
Logic
- Accuracy Evidence
- มุ่งเน้น การวิเคราะห์และประเมินข้อมูลอย่างถูกต้องประกอบเหตุผล
- ใช้เหตุผลและแสดงการคิดเชิงโครงสร้าง
- ให้ความสำคัญกับ ความแม่นยำ ความน่าเชื่อถือ
และความสอดคล้องเชิงตรรกะ
- ตรวจสอบ สมมติฐานและอคติ
- ตัดสินใจบนพื้นฐานของ หลักฐานและเหตุผล
- แสดงลักษณะ ตั้งคำถามและสงสัยประกอบเหตุผล
- ใช้ใน การตัดสินใจ การวิเคราะห์ และการแก้ปัญหา
📌
สรุป เน้น การประเมินและคัดกรองไอเดีย
เพื่อให้ได้ข้อสรุปที่แม่นยำและน่าเชื่อถือ
3.
ส่วนที่ซ้อนกัน Thinking Circuit (ส่วนสีเทากลาง) ความเชื่อมโยง
- Systematic
Problem Solving
- Cognitive
Adaptability
- Inquiry
Mindset
- Deep Understanding
- ใช้สำหรับ การแก้ปัญหาและการตัดสินใจ
- ต้องการ ใจเปิดกว้างและปรับตัวได้
- กระตุ้น ความอยากรู้อยากเห็นและการสำรวจ
- มุ่งเน้น ความชัดเจนและความเข้าใจเชิงลึก
- ใช้เหตุผลและกระบวนการคิดแบบมีโครงสร้าง
- ตั้งคำถามต่อสมมติฐานและพิจารณาทางเลือกอื่นได้สมเหตุสมผล
- แสดงให้เห็นว่า การคิดสร้างสรรค์ช่วยสร้างไอเดีย
ขณะที่การคิดเชิงวิพากษ์ช่วยประเมินและปรับแต่งไอเดียนั้นให้ชัดเจนตามหลักการที่ถูกต้อง
📌
สรุป
ทั้งสองหลักคิดจึงทำงานเสริมกัน สร้างไอเดีย → ประเมินและปรับปรุงไอเดีย
สามารถสรุปความสัมพันธ์โดยรวม ดังภาพ
2
- Creative
Thinking
= จุดเริ่มต้นของการสร้างแนวคิดใหม่
- Critical
Thinking
= ขั้นตอนต่อมาที่คัดกรองและทำให้แนวคิดใช้งานได้จริง
- Thinking
Circuit (เมื่อผสานกัน) → ได้กระบวนการคิดที่ครบวงจรคือ คิดได้ → วิเคราะห์ได้
→ ใช้ได้จริง
เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับการทำอาหาร สามารถจำแนกได้ดังนี้
- Creative
Thinking
= คิดเมนูใหม่ ๆ
-
Critical
Thinking
= ชิม ปรับรส และตรวจสอบคุณภาพก่อนเสิร์ฟ (บริการ)
- Thinking Circuit = วงจรการทำอาหารที่เชื่อมโยงตั้งแต่คิดเมนูจนถึงปรับปรุงสูตรและเสิร์ฟ เพื่อให้ได้อาหารที่รสชาติอร่อย พร้อมคุณค่าทางโภชนาการและคุณภาพสูงสุด วงจรการทำอาหารที่เชื่อมโยงตั้งแต่คิดเมนูจนถึงปรับปรุงสูตรและเสิร์ฟอย่างสร้างสรรค์ เพื่อให้ได้อาหารที่รสชาติอร่อย คุณภาพสูงสุด และบริการที่ประทับตราตรึงใจ
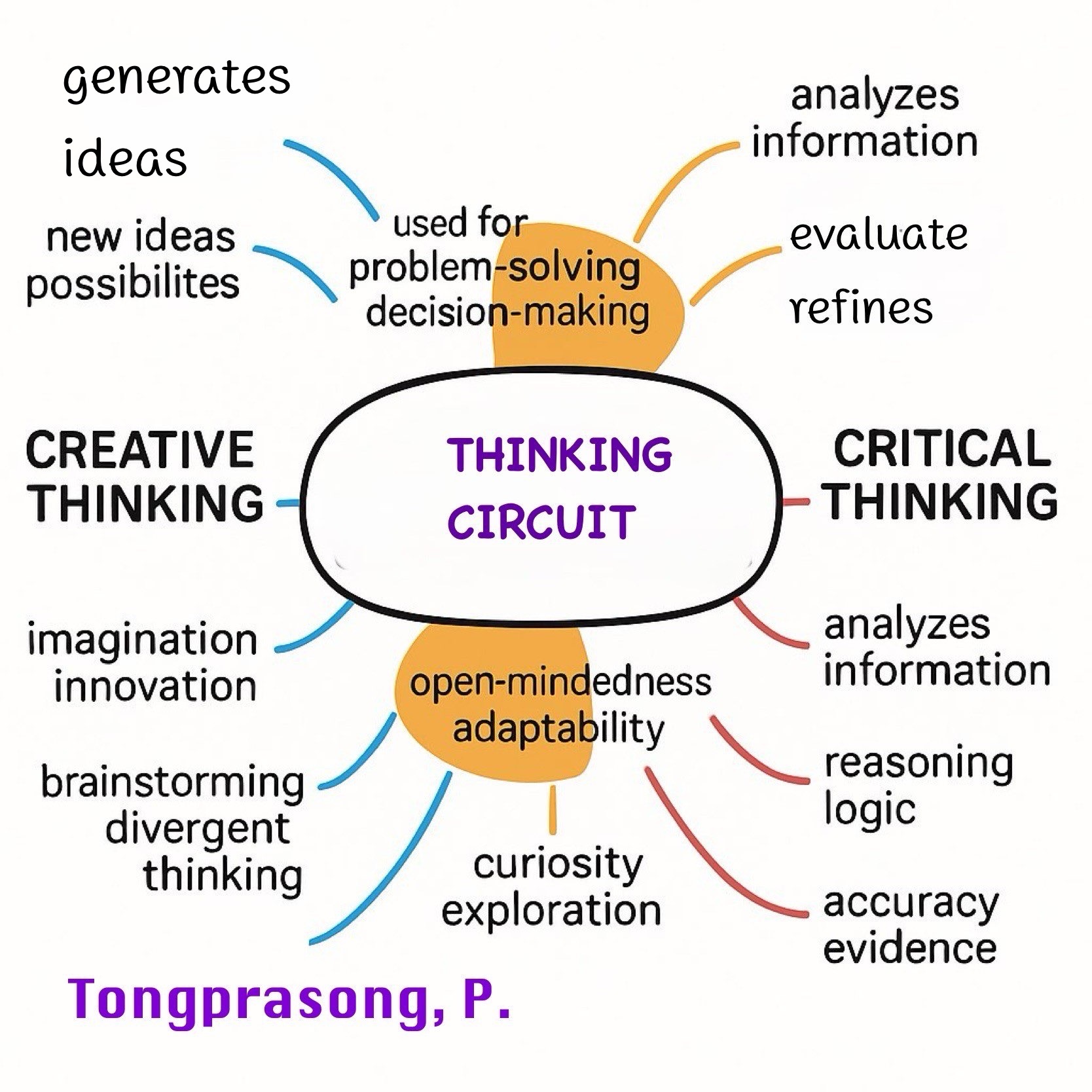
ภาพ 2 Mind
Map: Thinking Circuit
การคิดเชิงสร้างสรรค์
(Creative
Thinking) และการคิดเชิงวิพากษ์ (Critical
Thinking)
เป็นทักษะการคิดขั้นสูงสำคัญของศตวรรษที่ 21
ที่แสดงความสัมพันธ์และเสริมพลังกันอย่างใกล้ชิด Creative
Thinking มุ่งเน้นการสร้างแนวคิดใหม่ ความเป็นไปได้
และการแก้ปัญหาที่แปลกใหม่ ขณะที่ Critical Thinking มุ่งเน้นการวิเคราะห์
ประเมิน และปรับปรุงแนวคิดเหล่านั้นให้มีเหตุผล
ชัดเจน และสามารถนำไปใช้ได้จริง
การผสานทั้งสองทักษะทำให้เกิดกระบวนการแก้ปัญหาที่ครบวงจรและมีประสิทธิภาพ
นำไปสู่คุณภาพ และมาตรฐาน ซึ่งได้รับการยืนยันจากรายงานของ OECD (2025)
ที่ระบุว่า ความสามารถในการสร้าง ประเมิน
และปรับปรุงแนวคิดเป็นองค์ประกอบสำคัญของการคิดสร้างสรรค์ที่มีคุณภาพสูง
Thinking
Circuit
It enables the thinker to effectively link new knowledge with prior experiences, resulting in creative and sustainable problem-solving across various contexts.
Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking are essential 21st-century skills that are closely related and mutually reinforcing. Creative Thinking focuses on generating new ideas, possibilities, and novel solutions, while Critical Thinking emphasizes analyzing, evaluating, and refining those ideas to ensure they are logical, clear, and practical. The integration of these two skills produces a comprehensive and effective problem-solving process. This is supported by the OECD report (2025), which identifies the ability to generate, evaluate, and improve ideas as key components of high-quality creative thinking.
Recent studies have underscored the importance of integrating both skills. For instance, Shaber et al. (2025) investigated university students and found a significant positive correlation between Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking, recommending the parallel development of both skills. Similarly, Kuscu & Erdogan (2024) studied mathematics teachers before instruction and observed high levels of both skills, a moderate positive correlation, and that Creative Thinking predicted 23% of the variance in Critical Thinking.
Moreover, Thornhill-Miller et al. (2023) included Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking as part of the 4Cs, alongside Communication and Collaborationskills necessary for learning and working in the digital society of the 21st century. The integration of these skills not only helps learners think creatively and critically but also supports the development of other competencies essential for success in a rapidly changing digital world.
Key Characteristics of the Thinking Circuit
- It
is an iterative
thinking process involving continuous self-regulation.
- Its
main components include input
(information reception), processing, analysis and synthesis,
decision-making,
and feedback.
- It
supports both creative and critical thinking by balancing deep insights
and
diverse perspectives.
- It
promotes continuous learning and ongoing development.
1. Creative Thinking (Blue Circle - Left)
- Generates
ideas
- Explores
new possibilities
- Imagination
and innovation
- Brainstorming
and divergent thinking
2. Critical Thinking (Purple Circle - Right)
- Analyzes
information
- Evaluates
and refines
- Uses
reasoning and logic
- Ensures
accuracy and evidence
3. Thinking Circuit (Gray Overlapping Area - Center) The Connection
- Systematic
problem solving
- Cognitive
adaptability
- Inquiry
mindset
- Deep
understanding
Overall Relationship
- Creative
Thinking
= The
starting point for generating new ideas.
- Critical
Thinking
= The
subsequent step that filters and makes ideas practical and applicable.
- Thinking
Circuit
(Integration) = A complete thinking process: conceive → analyze → apply
effectively.
- Creative
Thinking
=
Inventing new recipes.
- Critical
Thinking
=
Tasting, adjusting flavors, and checking quality before serving.
- Thinking
Circuit = The
entire cooking cycle, linking recipe creation, continuous improvement,
and
serving to deliver delicious, high-quality food with memorable
presentation.
Recent research, such as Shaber et al. (2025), has reinforced the significance of developing these skills concurrently, demonstrating positive correlations between Creative Thinking and Critical Thinking. Kuscu & Erdogan (2024) also found that Creative Thinking could predict a significant portion of Critical Thinking variance among mathematics teachers. Furthermore, Thornhill-Miller et al. (2023) identify these two skills as part of the essential 4Cs alongside Communication and Collaboration for effective learning and working in the digital era.
The integration of Creative and Critical Thinking not only enhances learners ability to think innovatively and rationally but also supports the development of other competencies necessary for success in todays fast-changing digital society.
รายการอ้างอิง (References)
Kuscu,
H., & Erdogan, F.
(2024). Examination of Creative Thinking Skills and Critical Thinking
Dispositions of Pre-Service Mathematics Teachers. International
Journal of Progressive
Education, 20(5), 3855. https://doi.org/10.29329/ijpe.2024.1063.4
OECD.
(2025). Creative minds
in action:
Students imagination and ideas in storytelling, design and problem
solving
tasks on the PISA test. OECD Education Policy Perspectives.
OECD
Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/5b718eb2-en
Shaber,
N., Shah, S. K., Imran,
M., & Almusharraf, N. (2025). Exploring the relationship between
critical
thinking and creativity in university students: Gender differences and the
assessment of skills. Education
Sciences, 15(4), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15040464
Thornhill-Miller,
B., Camarda,
A., Mercier, M., Burkhardt, J.-M., Morisseau, T., Bourgeois-Bougrine,
S.,
Vinchon, F., El Hayek, S., Augereau-Landais, M., Mourey, F., Feybesse,
C.,
Sundquist, D., & Lubart, T. (2023). Creativity, critical thinking,
communication, and collaboration: Assessment, certification, and
promotion of
21st century skills for the future of work and education. Journal of
Intelligence,
11(3), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence11030054
》》》》》》》》》》
Asst.Prof. Phorramatpanyaprat Tongprasong, Ph.D., FHEA UKPSF
Suan Dusit University,
295 Nakhonratchasima RD., Dusit,
Dusit, BKK, Thailand 10300.
TEL. +6622445748
https://musterverse.dusit.ac.th/
phorramatpanypaprat_ton@dusit.ac.th
phorramatpanyaprat@gmail.com
》》》》》》》》》》
LINE OA @mustland
Since, 2025